Exosomes
FAQ
Exosomes are tiny extracellular vesicles released by almost all cell types in the body. They serve as communication carriers, transporting proteins, lipids, and genetic material between cells. This communication is crucial for various biological processes, including immune response, tissue repair, and cell signaling. Additionally, exosomes are being explored for their potential in disease diagnostics and therapeutic applications.
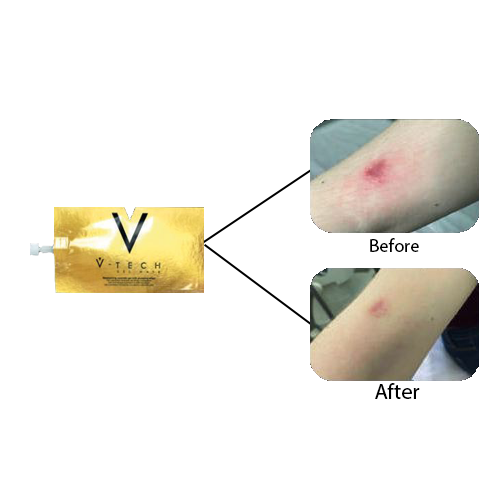
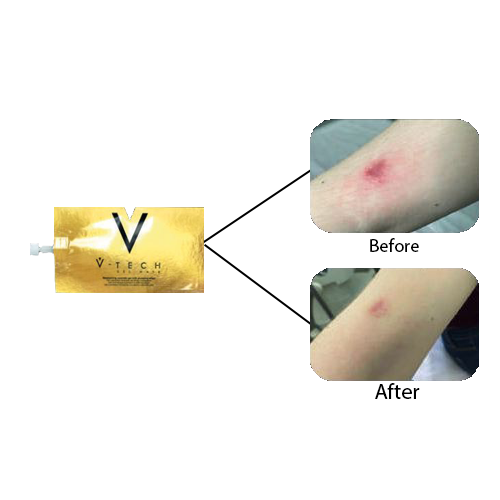
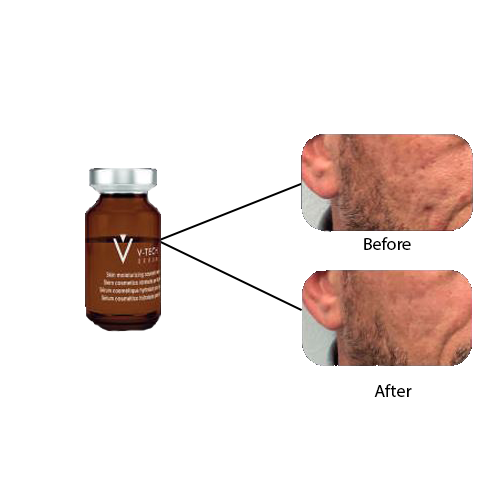
Exosomes have significant potential in medical applications. They are being studied as biomarkers for early diagnosis of diseases like cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. In therapeutics, they can be engineered to deliver drugs to specific cells, making treatments more targeted and effective. Exosomes derived from stem cells are also being utilized in regenerative medicine for tissue repair and anti-aging therapies.